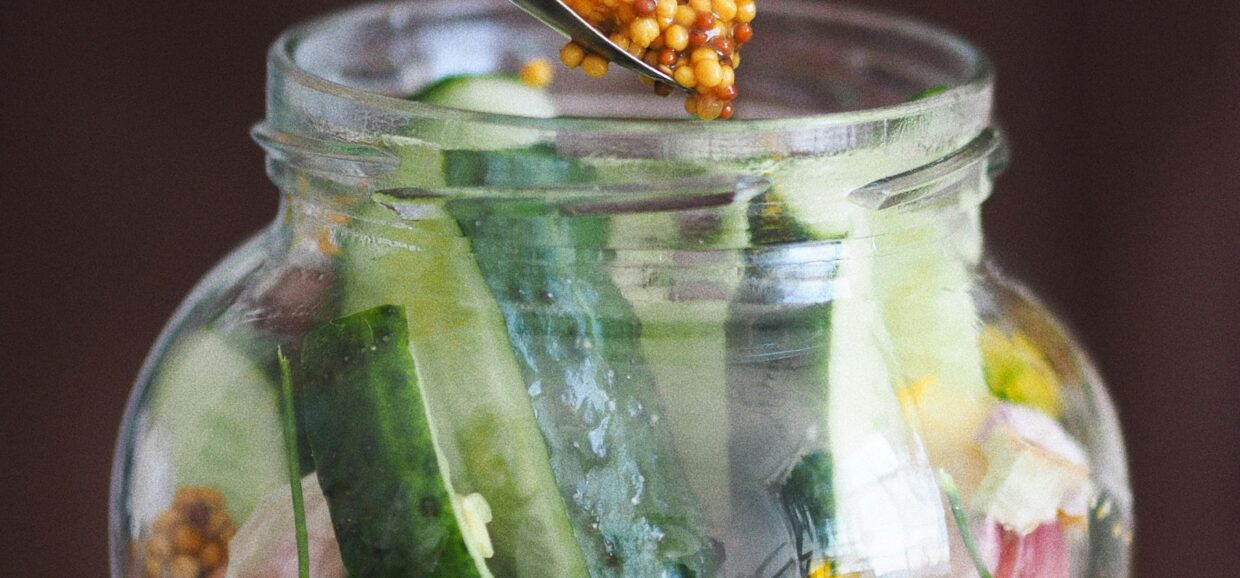Fermented foods have been cherished across cultures for centuries, not only for their unique flavors but also for their remarkable health benefits. From improving digestion to boosting immunity, incorporating fermented foods into your diet can be a game-changer. Plus, making them at home is both fun and rewarding. Let’s dive into the world of fermentation and discover how you can start your own culinary adventure.
Health Benefits of Fermented Foods
- Enhanced Gut Health: Fermented foods are rich in probiotics—beneficial bacteria that support a healthy gut microbiome. A balanced gut can improve digestion and may reduce the risk of certain diseases.
- Boosted Immune System: A significant portion of the immune system is linked to gut health. Regular consumption of fermented foods can strengthen immunity and help the body fend off infections.
- Improved Mental Well-being: Emerging research suggests a connection between gut health and mental health. Probiotics found in fermented foods may help alleviate symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Nutrient Absorption: Fermentation can increase the bioavailability of nutrients, making it easier for the body to absorb essential vitamins and minerals.
Popular Fermented Foods and Their Benefits
- Yogurt: Rich in probiotics like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, yogurt aids digestion and supports immune health.

- Kefir: A fermented milk beverage containing various bacterial strains and yeasts, beneficial for digestion and bone health.

- Kimchi: A spicy fermented cabbage dish from Korea, loaded with vitamins A and C, and known for its immune-boosting properties.

- Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage rich in fiber, vitamins, and probiotics, promoting digestive health.

DIY Fermentation: How to Get Started
Embarking on home fermentation is simpler than you might think. Here’s a basic guide to fermenting vegetables:
1. Gather Your Ingredients and Equipment
- Fresh Vegetables: Cabbage, carrots, cucumbers, or radishes are excellent choices.
- Non-iodized salt: Such as sea salt or pickling salt.
- Filtered Water: Chlorine-free water is essential for proper fermentation.
- Clean Glass Jars: Mason jars work well.
2. Prepare the Vegetables
- Wash Thoroughly: Clean your chosen vegetables under running water.
- Chop or Shred: Cut vegetables into desired shapes and sizes.
3. Create a Brine
Dissolve 1-3 tablespoons of non-iodized salt in a quart (about 1 liter) of filtered water. The salt concentration can be adjusted based on taste and the type of vegetable.
4. Pack the Jars
- Add Vegetables: Place the prepared vegetables into the clean jars, leaving about an inch of headspace.
- Pour Brine: Ensure the vegetables are fully submerged under the brine to prevent mold growth.
5. Ferment
- Cover Loosely: Seal the jars with lids, but not too tightly, to allow gases to escape.
- Store: Keep the jars at room temperature, away from direct sunlight, for 3-10 days. The duration depends on the vegetable and your taste preference.
6. Taste and Refrigerate
- Sample: After a few days, taste your ferment. Once it reaches the desired flavor, transfer the jars to the refrigerator to slow down fermentation.
Safety Tips
- Cleanliness: Ensure all equipment is thoroughly cleaned to prevent unwanted bacteria.
- Submersion: Always keep vegetables submerged under the brine to avoid mold.
- Observation: If you notice an off smell, discoloration, or mold, discard the batch and try again.
Incorporating fermented foods into your diet is a delightful way to enhance flavor and boost health. With simple ingredients and patience, you can create nutritious fermented delights in your kitchen. Start your fermentation journey today and experience the myriad benefits these age-old foods have to offer.